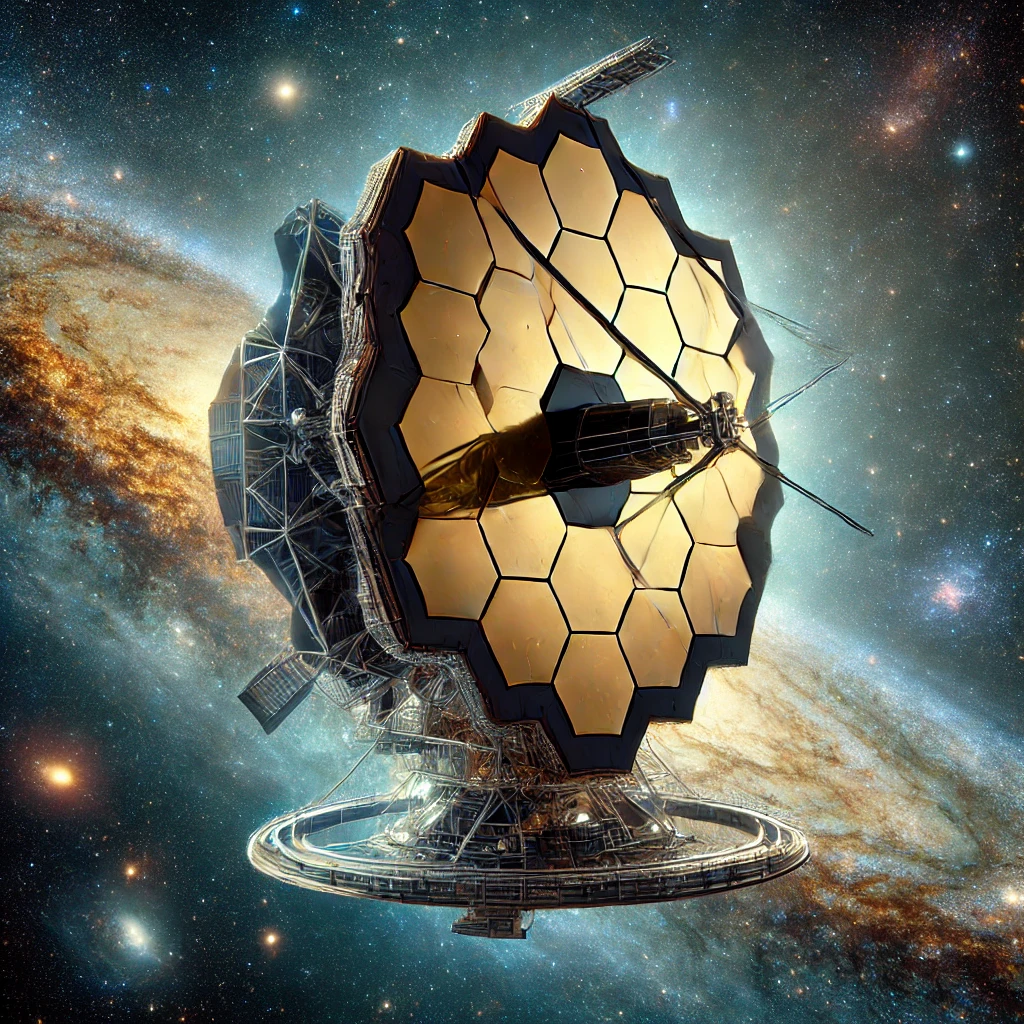
The James Webb Space Telescope or JWST, as it is also referred to often, being dubbed as the successor to the Hubble Space Telescope takes that very quest a notch higher in levels. This international collaboration led by NASA includes crucial inputs from the European Space Agency and the Canadian Space Agency, launched on December 25, 2021. While Hubble observes mainly in visible and ultraviolet light, JWST operates primarily in the infrared spectrum and thus can look behind cosmic dust and uncover phenomena previously invisible to our view.
Key Features of JWST
The JWST is equipped with some of the most sophisticated technologies:
- Primary Mirror: The telescope’s 6.5-meter-wide segmented mirror, of beryllium, coated in gold to reflect light back, is designed to capture faint light from early galaxies.
- Instrumentation: JWST hosts four main instruments: NIRCam, for the Near Infrared Camera; NIRSpec, for the Near Infrared Spectrograph; MIRI, for the Mid-Infrared Instrument; and FGS/NIRISS, a Fine Guidance Sensor coupled with a Near Infrared Imager and Slitless Spectrograph. These allow for the great capture of high-resolution images and spectra of objects in a wide range of wavelengths.
Location: At 1.5 million kilometers from Earth, located in the second Lagrange point (L2), JWST is in a stable environment with minimum interference from Earth and the Sun.
That combination of state-of-the-art features in one observatory allows it to sense faint signals from millions of light-years away.
Historic Discoveries Made by JWST
Since its launch in July of 2022, the James Webb Space Telescope has been giving us some of the most breathtaking observations that completely revolutionize our understanding of the universe for instance:
1. First Galaxies and First Stars Formed
JWST had looked farther back in time than any other telescope ever has and had captured images of some of the earliest galaxies formed just a few hundred million years after the Big Bang. Among the discoveries of the planet is CEERS-93316 that formed just 235 million years after the Big Bang. The galaxies are more mature than initially thought, thus forcing scientists to rethink their models of galactic evolution.
2. Star-Birth Regions and Exoplanets
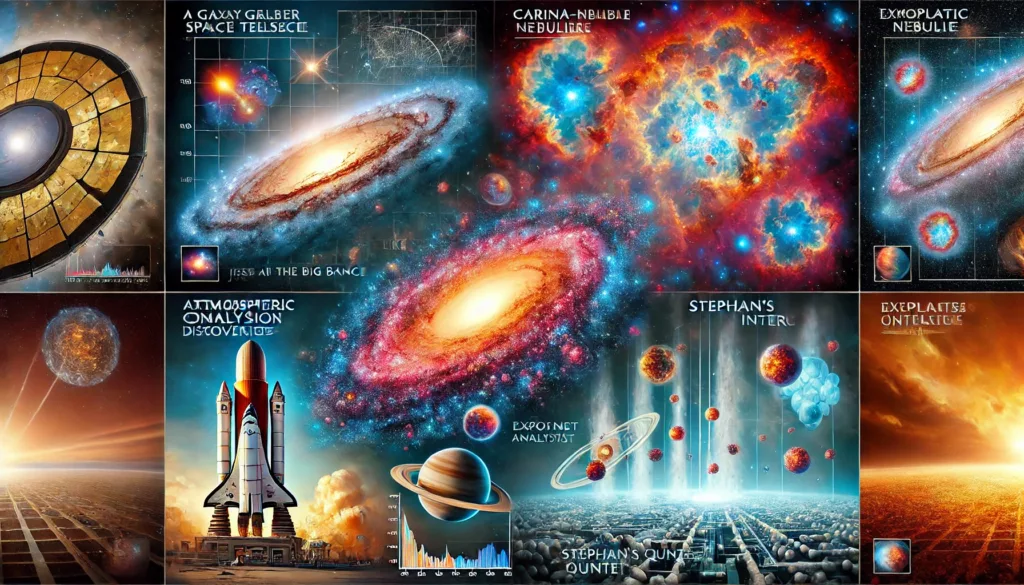
Investigating star formation and the formation of planetary systems is another critical focus for JWST. Since JWST can penetrate thick clouds of dust it has already revealed close-up images of stellar nurseries, such as the well-known Carina Nebula and the more spectacular Tarantula Nebula where stars are born. Because the images produced are so sharp, astronomers will see granular details about how stars are formed and evolve in time.
The telescope has also revolutionized the study of exoplanets, that is, planets outside our solar system. It has analyzed atmospheres of several exoplanets, detailing the presence of water vapor, carbon dioxide, and other molecules. One of its biggest successes in this area is the detailed atmospheric studies of WASP-39b, where JWST has provided the first clear detection of carbon dioxide on an exoplanet.
- Water in Distant Worlds
Infrared sensitivity will enable JWST to make routine identifications of the signatures of water in distant worlds. One of its first triumphs was the detection of vaporized water in an atmosphere within the exoplanet WASP-96b, a gas giant 1,150 light-years away from Earth. This discovery could potentially lead the way to the observation of smaller, thus potentially habitable exoplanets in the future. - Galaxies in Motion
Another powerful theme for JWST is the dynamics of galaxies and their interactions over cosmic time. Distant galaxies have been viewed in terrific detail as a way of understanding how they are formed, merge together, and evolve. The sharpest view to date of Stephan’s Quintet, five galaxies caught up in a cosmic dance, was supplied by JWST. Such observations not only demonstrate the richness of their interaction but, in addition, unveil some previously unseen features; for example, galaxy collisions do provoke big shock waves.
5. Early Universe Explored
Perhaps one of the profoundest achievements of James Webb JWST is that it has enabled humanity to look deep back into the universe at its earliest moments. Observations from redshifted light coming from ancient galaxies tell us a great deal about the first billion years in the cycle of the universe. The data will allow us to grasp galaxy formation, super-massive black hole evolution, and how large scales of the cosmos were assembled.
- Planetary Science and Our Solar System
Besides observing deep space, the James Webb will also examine the planets in our solar system. It has taken images of *Jupiter*, the cloud-patterned planet, at unprecedented resolution for its turbulent atmosphere, auroras, and faint rings. For the future, the telescope will examine the icy moons of *Europa* and Enceladus, two of the leading contenders to host microbial life because of their subsurface oceans.
The Future of Space Exploration with JWST
JWST is still in its infancy with regard to the mission and yet discoveries over the past year have already exceeded the expectations set for this far-reaching enterprise. Over the next few decades, JWST will venture deeper into questions that astronomers pose today-concerning dark matter, the universe’s future fate, and perhaps, life elsewhere. Its revolutionary infrared ability will allow scientists to probe cosmic secrets deeper, enabling further refinement of our cosmological models of how the universe works.
As each of these breathtaking images and groundbreaking pieces of data rolls into our feeds, it stands as testament to the ingenuity and collaboration of humanity. It is an exploration device and an inspirational beacon for generations in coming centuries to look up at the stars and contemplate the unknowns that lie beyond.
Conclusion
The James Webb Space Telescope marks a paradigm in space exploration-a view of the earliest epochs of the universe and the complex processes that shape the galaxies, stars, and planets. From ancient galaxies as detected to the atmospheres of exoplanets, it changes everything known to date. As we wait to see more out of this incredible observatory, it is clear that JWST will be the cornerstone of astronomical research for decades to come.
More News: Space


