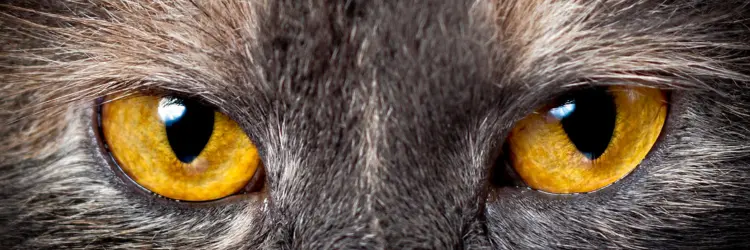
In a leap towards smarter autonomous navigation, Korean researchers have developed a cutting-edge vision system for drones and robots, inspired by the structure of a cat’s eye. The design, led by Professor Young Min Song from the Gwangju Institute of Science and Technology (GIST), offers advanced object detection and recognition through a slit-like aperture and reflective layer. This innovation not only enhances visibility in varying light but also reduces energy demands, making it a practical breakthrough for robotic technology.
Why Cats’ Eyes Are the Model for Robotic Vision
Autonomous systems like drones, security robots, and self-driving cars face one common challenge: adapting to changing lighting conditions. Whether under intense sunlight, low-light environments, or amidst a cluttered background, these machines struggle to process visual information effectively. Nature, however, has perfected this ability—particularly in cats.
Felines have evolved with highly specialized eyes that perform remarkably well in various lighting scenarios. By day, their vertical, slit-shaped pupils focus sharply, reducing glare. At night, their pupils expand, maximizing light intake, while a reflective layer known as the tapetum lucidum enhances their night vision, giving their eyes a glowing quality.
The GIST team, inspired by this natural marvel, designed a lens system that mimics these feline traits to give robots similar adaptability and efficiency. This system holds potential for a broad range of applications, from improving drone navigation to empowering rescue robots in low-visibility scenarios.
Advancing Robotic Vision: From Concept to Reality
The core of this feline-inspired technology lies in its unique lens and sensor system. By utilizing a slit-like aperture, much like a cat’s vertical pupils, this design effectively filters excess light and focuses on key objects. Additionally, a reflective layer akin to the tapetum lucidum improves low-light visibility, ensuring clear sight across different environments.
This breakthrough was recently documented in Science Advances, marking a pivotal achievement in the field of artificial vision. The robotic vision system not only boosts object recognition but does so with minimal energy by leveraging optical design rather than complex computational processing.
Impact and Applications: A Future Shaped by Smarter Robots
According to Professor Song, “Robotic cameras often struggle to spot objects in busy or camouflaged backgrounds, especially when lighting conditions change. Our design solves this by letting robots blur out unnecessary details and focus on important objects.” This efficiency opens the door to a range of real-world uses where precision and energy savings are critical.
For instance, in search-and-rescue missions, drones equipped with this advanced system could navigate dense forests or dark tunnels, efficiently spotting survivors. Security robots could benefit, too, from detecting motion or suspicious activity in low-light environments. This technology also holds promise for industrial monitoring, providing a smarter way to detect issues on production lines or large-scale facilities.
In the long term, these advanced robotic eyes could revolutionize autonomous driving systems, improving object recognition and reaction time in challenging conditions like fog or at night. Professor Song envisions this innovation as a potential replacement for human oversight in risky or intensive tasks, giving robots the power to navigate complex situations with enhanced accuracy.
A Glimpse into the Future of Autonomous Technology
The concept of cat-inspired robotic vision is a prime example of how biomimicry—adapting nature’s designs for human technology—can lead to remarkable breakthroughs. With enhanced object detection and energy efficiency, these “robotic cat eyes” pave the way for more capable autonomous machines, setting new standards in fields as diverse as robotics, security, and transportation.
For More Updates: Emerging Technologies