In the realm of robotics, the realization of seemingly simple tasks that humans effortlessly perform introduces a complex challenge for robotic systems. To address this, the field of robotic learning has gained momentum, aiming to develop more adaptable and capable robotic systems. Notably, Google DeepMind robotics team made a significant breakthrough with their Robotics Transformer (RT-1) last year.
The team trained their Everyday Robot systems using a database of 130,000 demonstrations, enabling them to perform tasks like picking and placing objects and opening drawers with an impressive 97% success rate for over 700 tasks.
Building upon the success of RT-1, DeepMind is now unveiling the next iteration, RT-2, with even more advanced capabilities. One of the key advancements is the ability of robots to transfer concepts learned from relatively small datasets to different scenarios successfully.
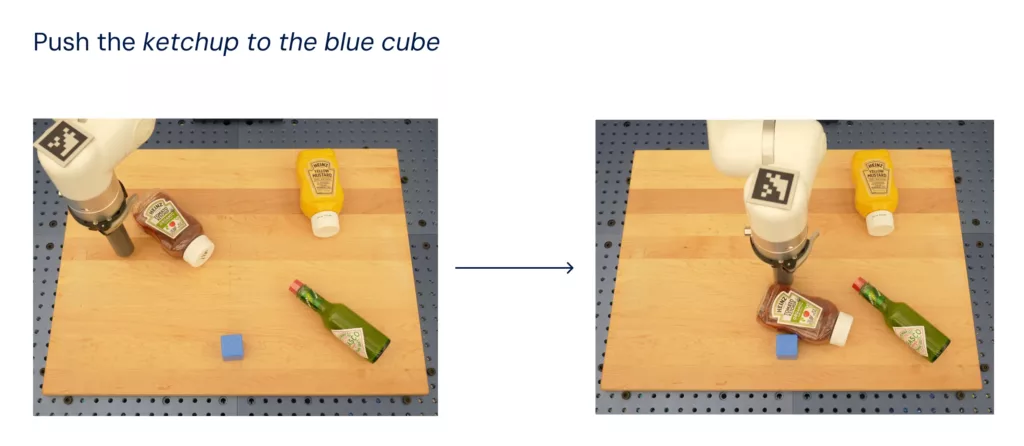
This means that RT-2 can interpret new commands and respond to user instructions with a rudimentary understanding of object categories or high-level descriptions. Essentially, the system has the capacity to reason about objects and their context, allowing for more intelligent and context-aware responses.
A remarkable aspect of RT-2 is its ability to determine the most suitable approach for novel tasks based on existing contextual information. For example, if a robot is asked to throw away trash, traditionally, it would require explicit training to identify what qualifies as trash and then execute the disposal task.
However, Google DeepMind RT-2 leverages knowledge from a vast corpus of web data, allowing it to identify trash without the need for specific training. This demonstrates the system’s capability to understand abstract concepts and generalize knowledge from various sources, making it more versatile in executing a wide range of tasks.
Vincent Vanhoucke, DeepMind’s Distinguished Scientist and Head of Robotics, explains that RT-2’s efficacy rate for executing new tasks has significantly improved from 32% in RT-1 to an impressive 62% in RT-2. This progress marks a significant step forward in robotic learning and showcases the potential for adaptable, context-aware robots that can navigate real-world scenarios with greater ease and intelligence.
Read More: News on Artificial Intelligence
As the field of robotic learning continues to evolve, we can anticipate further advancements and refinements, unlocking new possibilities for robotics in various industries and applications.
The ability to learn from limited datasets and adapt to diverse environments promises to revolutionize the way robots interact with the world and offer new solutions to complex challenges.


